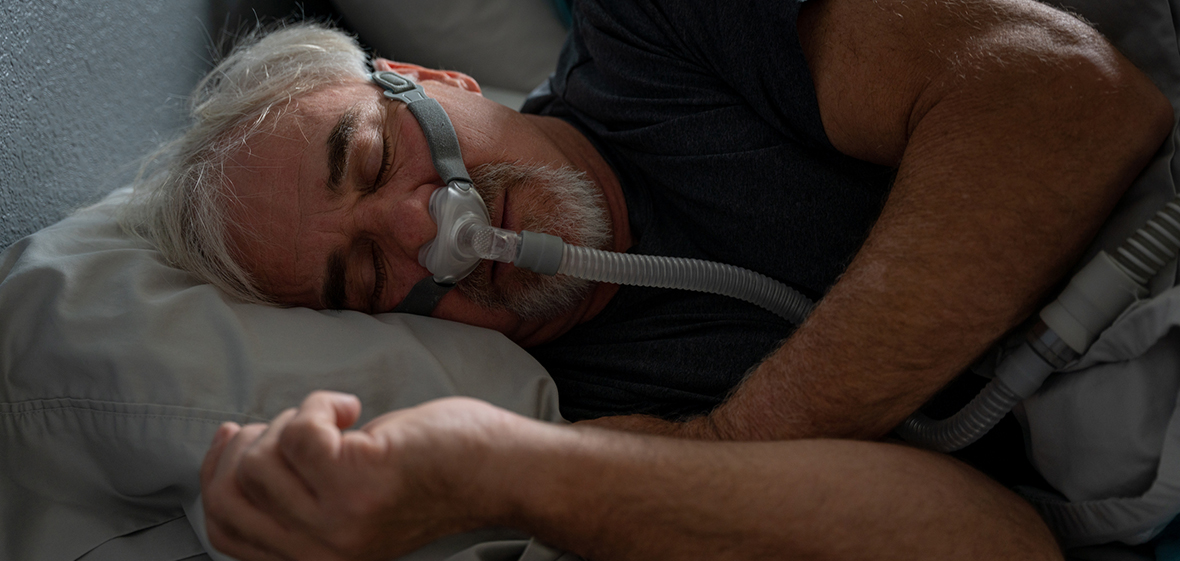
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that occurs when someone has one or more pauses in breathing while sleeping. The two main types of sleep apnea are obstructive and central. The most common type, obstructive sleep apnea, is caused by a blockage of the airway.
What are the symptoms of sleep apnea?
The most common signs and symptoms of sleep apnea are:
- Snoring
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Waking up frequently to urinate
- Poor memory (“brain fog”)
- Apneas (pauses in breathing)
- Morning headaches
- Poor cognition
- Poor mood
- Restless sleep
- Weight gain
These sleep disorder symptoms are often chalked up to a busy life, but feeling tired all the time may be a sign of something else. Those with sleep apnea may fight sleepiness during the day, whether at work or even while driving. Seeking the help of a sleep specialist is the key to identifying and treating sleep disorders.
How is sleep apnea treated?
If diagnosed with sleep apnea, our providers can recommend several options for treatment:
- Lifestyle changes/weight loss
- Positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy
- Oral appliances
- Positional therapy
- Upper airway stimulation device
- Surgery
- Expiratory positive airway pressure (EPAP) device
- Other
The goal of treating sleep apnea is to restore breathing during sleep and normalize the oxygen level. PAP therapy is the most common treatment for moderate to severe sleep apnea in adults. Using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine while sleeping will keep your airway open through a gentle stream of air blowing into your airway.
There are many types of CPAP machines and masks. If PAP therapy is recommended, our team will work with you to find the best type for you.
What happens if my sleep apnea goes untreated?
Sleep apnea can cause or worsen high blood pressure and other cardiovascular diseases, stroke, diabetes, obesity, depression and other medical conditions. It may also be responsible for impaired concentration, reduced alertness and slower reaction time, and it has been linked to an increase in motor vehicle accidents.
Untreated or under-treated sleep apnea causes premature death. Adequate treatment helps you have a normal lifespan and improves other medical disorders. Untreated sleep apnea is now a risk factor for dementia.
Our brain and body need enough deep sleep to optimize performance and prevent illness and disease. While we sleep, our body repairs, rejuvenates and restores itself, and when that process is disrupted, it can have long-lasting consequences. If you’re having trouble sleeping, excessive daytime drowsiness or chronic snoring, contact our offices to get started on a path to better sleep.
Important Considerations
- Continued follow-up is important once established on PAP therapy to ensure adequate treatment.
- Adequate overall sleep is critical. Most adults need seven to nine hours of sleep each night. Treatment for sleep apnea should be used with all sleep, including any naps if taken.
- Never drive or operate machinery when sleepy or drowsy.
- Notify all health care providers, especially surgeons and anesthesiologists, about your sleep apnea diagnosis. If you are using a PAP device, make sure to take it with you for all surgeries and procedures.
UofL Health – Sleep Medicine uses a multidisciplinary approach to diagnose and treat sleep disorders. Our physicians are board-certified by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. Call UofL Physicians – Sleep Medicine Associates at 502-259-6610 or UofL Physicians – Sleep Center at 502-588-0480 for more information or to schedule a sleep consultation.









