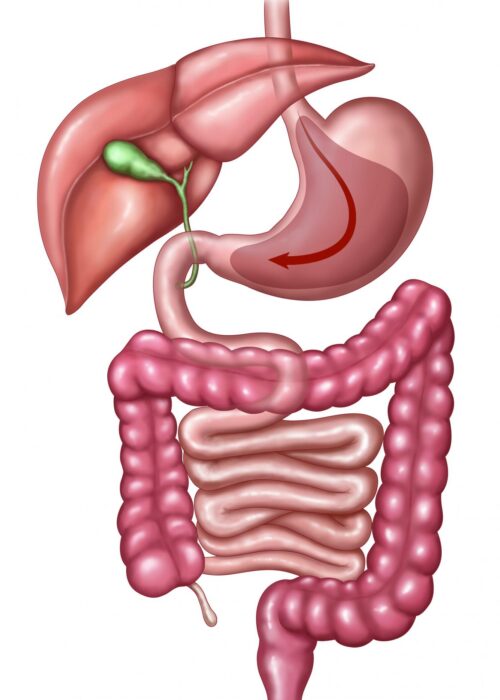
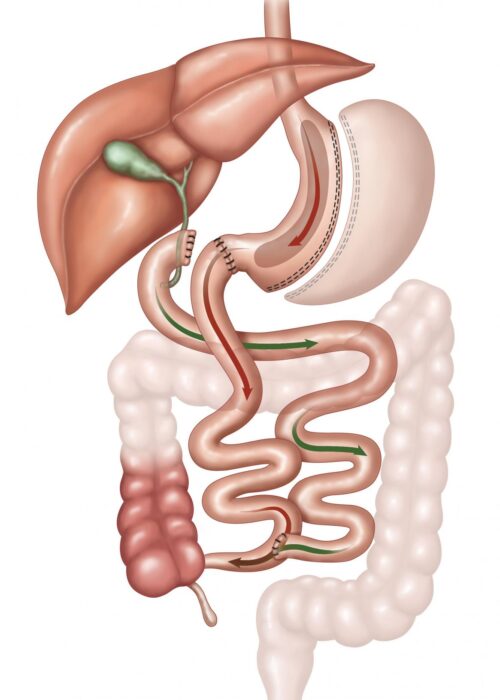
In a Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD-DS) procedure, a sleeve-like stomach is created and the duodenum is separated from the stomach. A part of the small intestine is then brought up and attached to the outlet of the newly created stomach so that food goes through the sleeve pouch and into the latter part of the small intestine. The small bowel segment that empties the bypassed small intestine is connected into the small bowel downstream.
What are the advantages of a BPD-DS procedure?
- Among the best results for improving obesity
- Affects bowel hormones to cause less hunger and more fullness after eating
- The most effective procedure for treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
What are the risks of a BPD-DS procedure?
- BPD-DS has slightly higher complication rates than other bariatric procedures
- Malabsorption
- Vitamin and micro-nutrient deficiencies
- Reflux and heart burn can develop or worsen
- Looser and more frequent bowel movements


