What is a Concussion?
A concussion, or mild traumatic brain injury, is caused by a direct hit or force to the head, face, neck or another part of the body that causes the head and brain to move quickly back and forth. It can result in a temporary disruption to normal brain functioning. A mild head injury is actually quite common and rarely results in any permanent brain damage.
Motor vehicle accidents, falls and sports injuries are common causes of concussions.
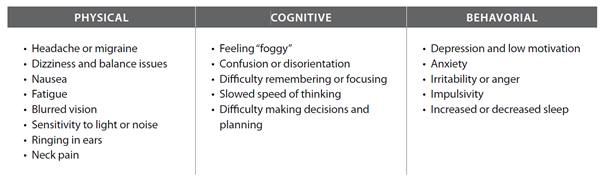
Symptoms of concussion can occur immediately or a few hours to days later. A concussion can cause physical symptoms and affect thinking/cognition, mood, and sleep.
What are the signs of a medical emergency?
Watch for signs of a more serious brain injury and report to a hospital if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Slurred speech
- Seizures
- Extreme loss of balance
- Repeated vomiting
- Loss of consciousness
- Worsening, throbbing headache
- Weakness/numbness in arms or legs
- Difficulty being awakened
- Increased confusion
- Dramatic behavioral change
- Unequal pupil size or decreased reactivity to light
UofL Health is ready to provide emergency care close to home when you need it. Click here to choose a location close to your home.
When do I seek follow-up care?
Generally, a primary healthcare provider may see you 1 to 2 weeks after the injury to monitor your symptoms and ensure recovery is going as expected.
If you are an athlete, even if the injury happened out of athletics, you should immediately follow up with your school’s certified athletic trainer. Your athletic trainer will help coordinate care with the appropriate sports medicine-trained physician. The certified athletic trainer and physician will work together to initiate a specific concussion management protocol for both return-to-learn strategies and supervised return-to-play protocol. Additional information regarding sports-specific concussion management can be here.
Sometimes people may need to see additional healthcare providers who are experienced in treating concussion patients to help manage specific symptoms.
Questions? See our frequently asked questions.


